Rows: 344
Columns: 8
$ species <fct> Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adel…
$ island <fct> Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgerse…
$ bill_length_mm <dbl> 39.1, 39.5, 40.3, NA, 36.7, 39.3, 38.9, 39.2, 34.1, …
$ bill_depth_mm <dbl> 18.7, 17.4, 18.0, NA, 19.3, 20.6, 17.8, 19.6, 18.1, …
$ flipper_length_mm <int> 181, 186, 195, NA, 193, 190, 181, 195, 193, 190, 186…
$ body_mass_g <int> 3750, 3800, 3250, NA, 3450, 3650, 3625, 4675, 3475, …
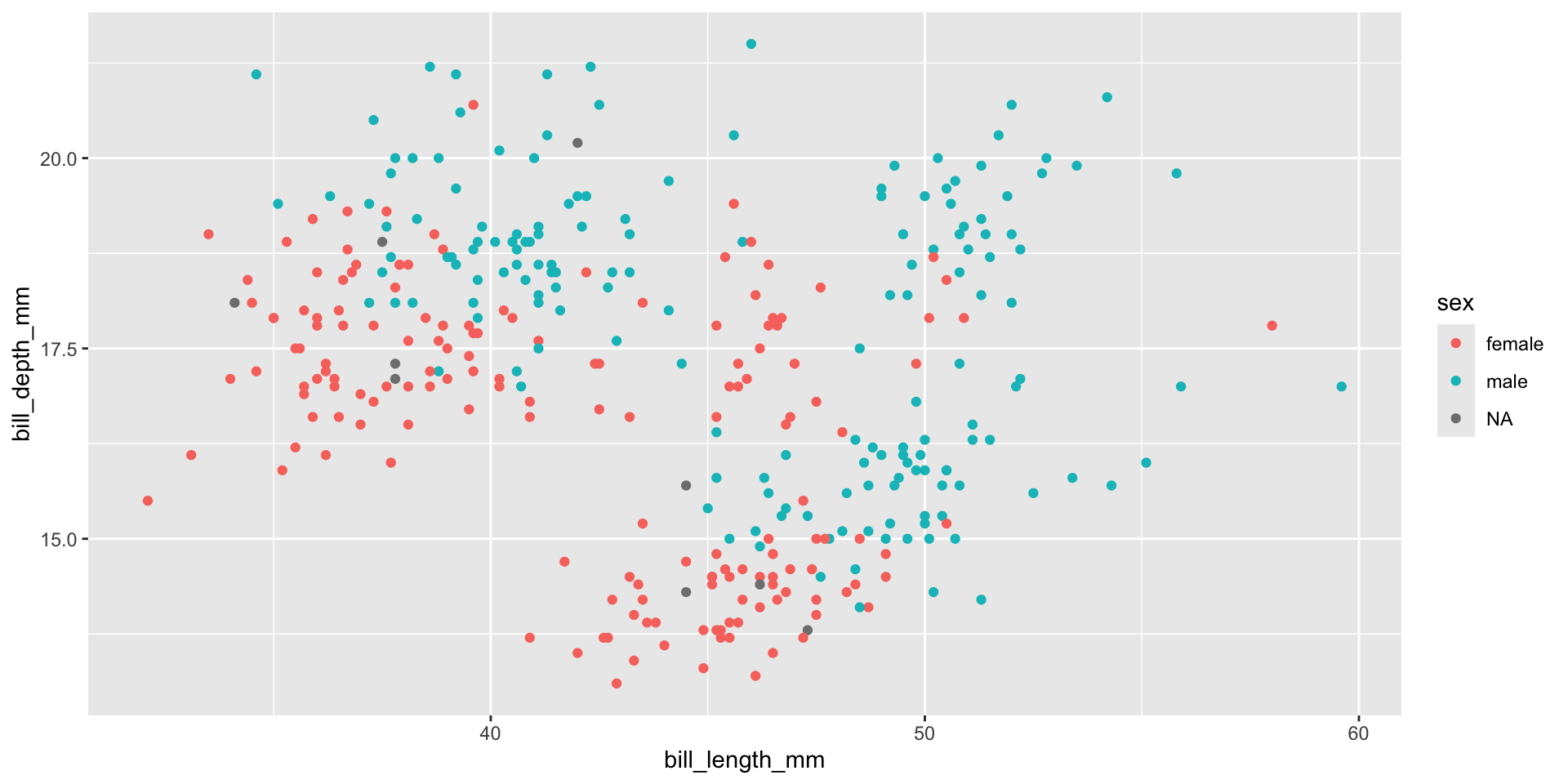
$ sex <fct> male, female, female, NA, female, male, female, male…
$ year <int> 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007…DATA VISUALIZATION
USING GGPLOT
2 Days Data Science Workshop at Institute of Development Studies, Jaipur (ICSSR)
“The simple graph has brought more information to the data analyst’s mind than any other device.” — John Tukey
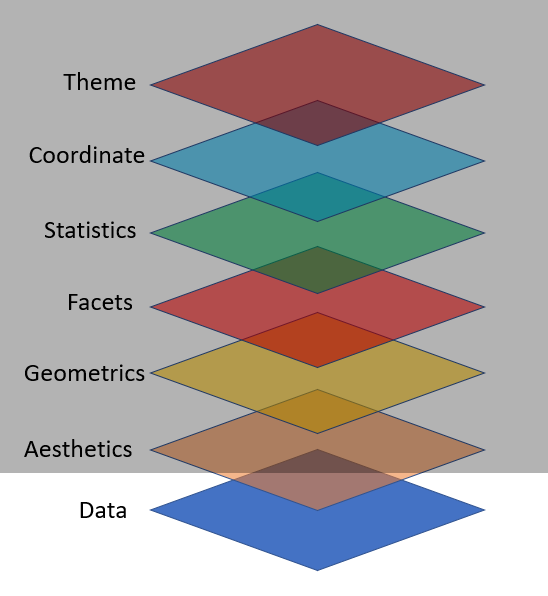
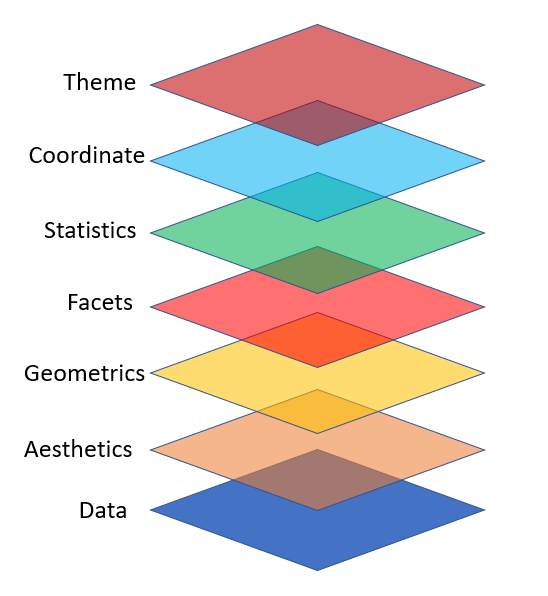
Grammar of Graphics

ggplot2 Layers
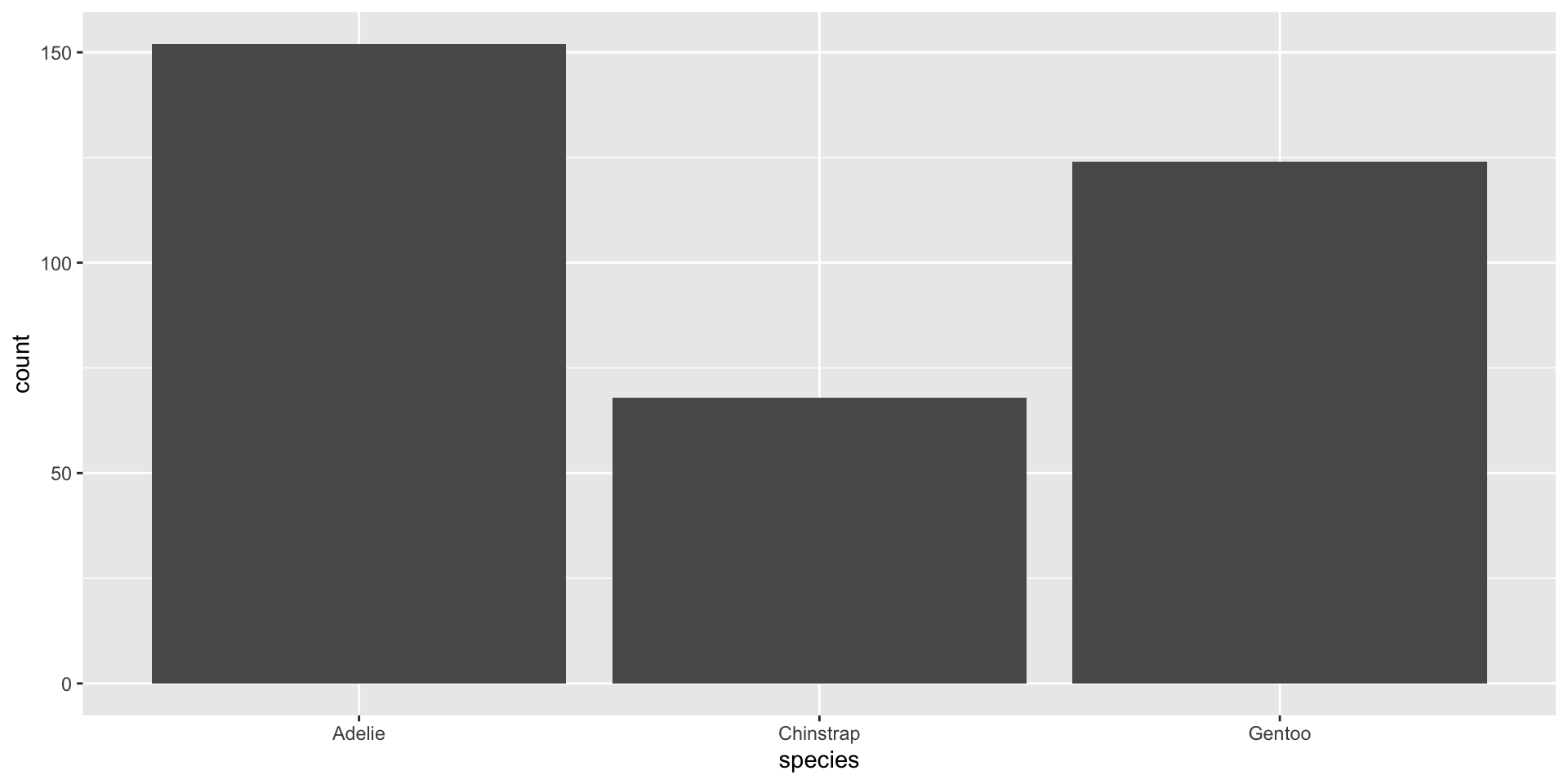
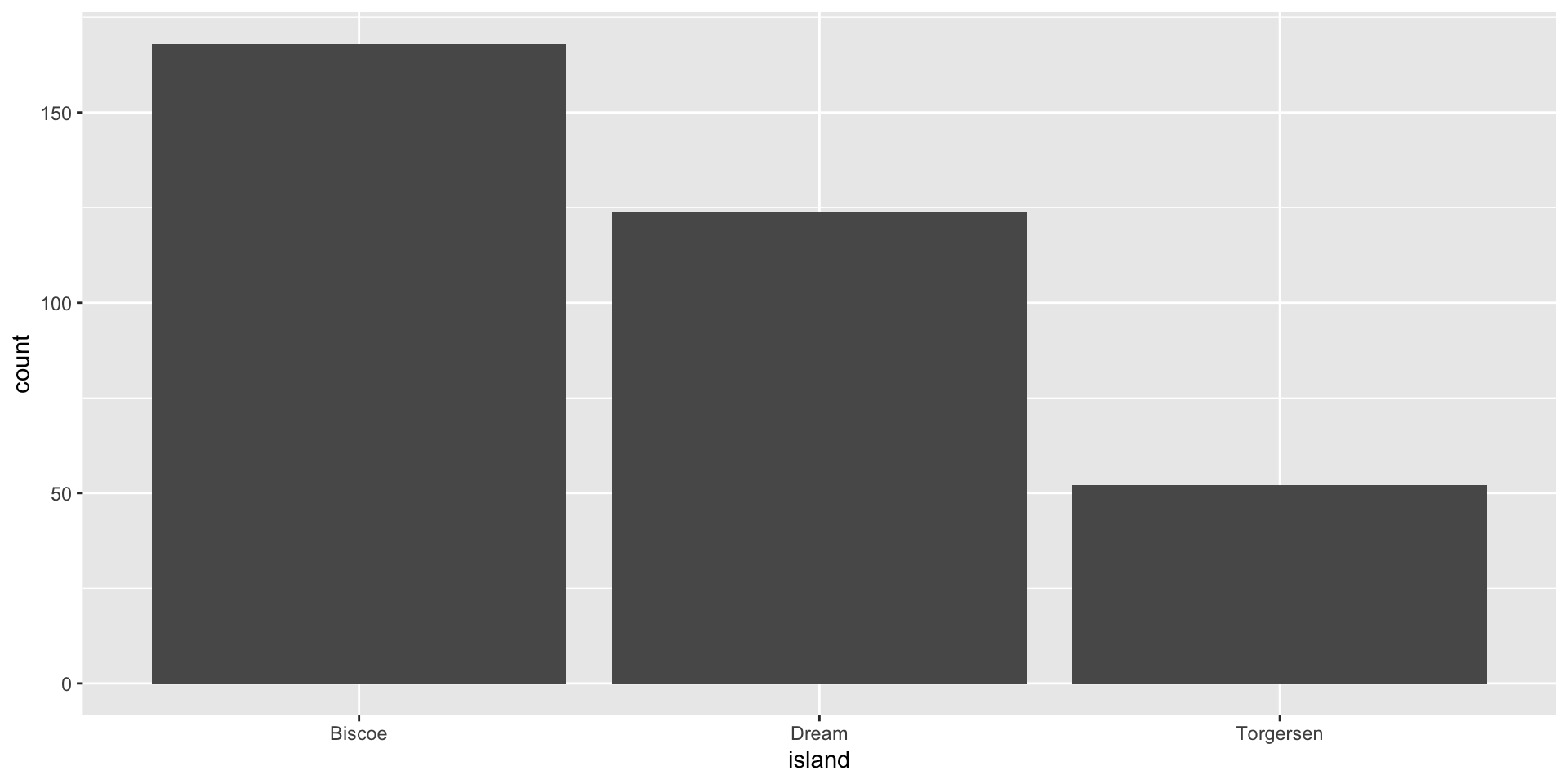
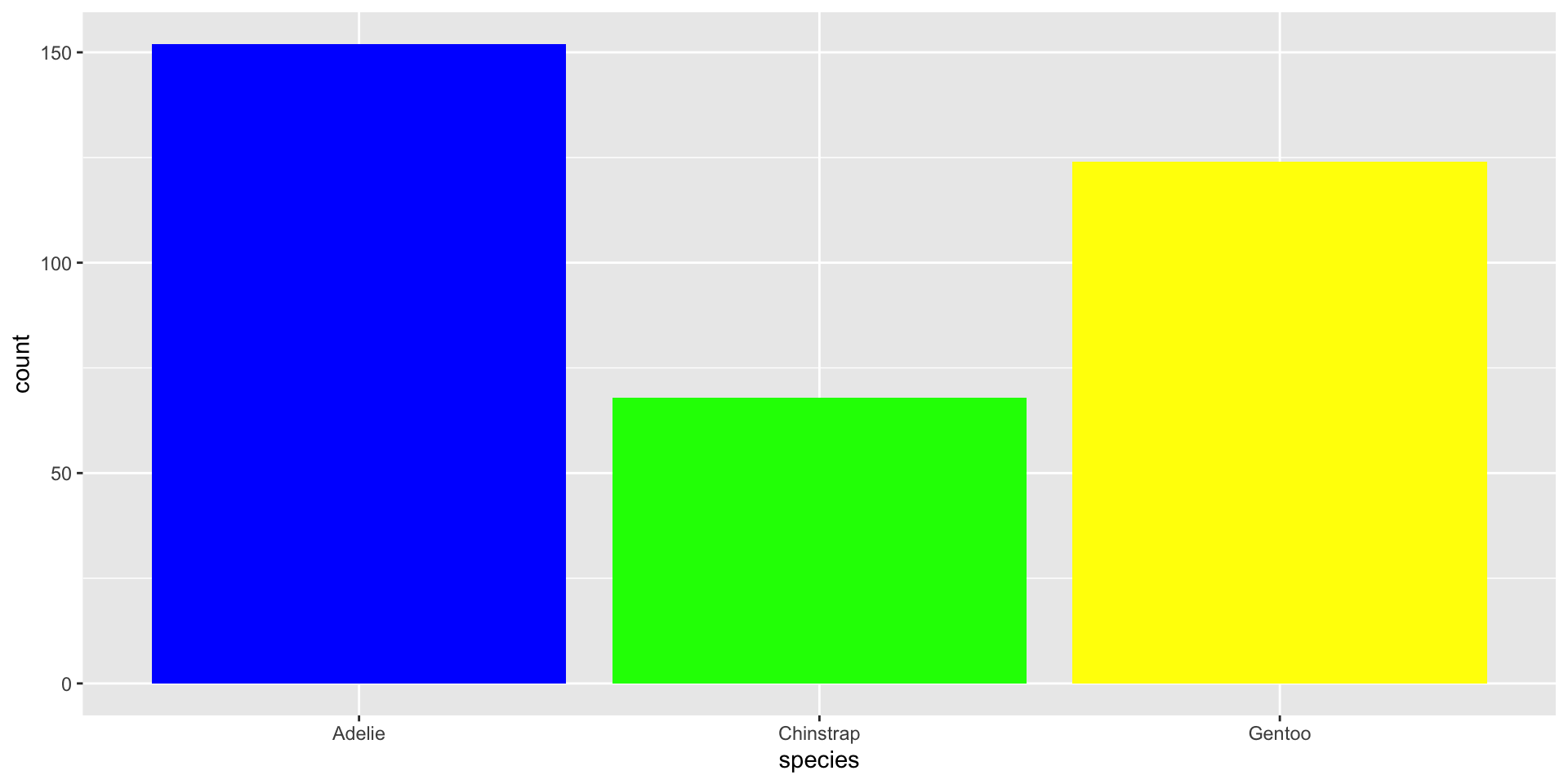
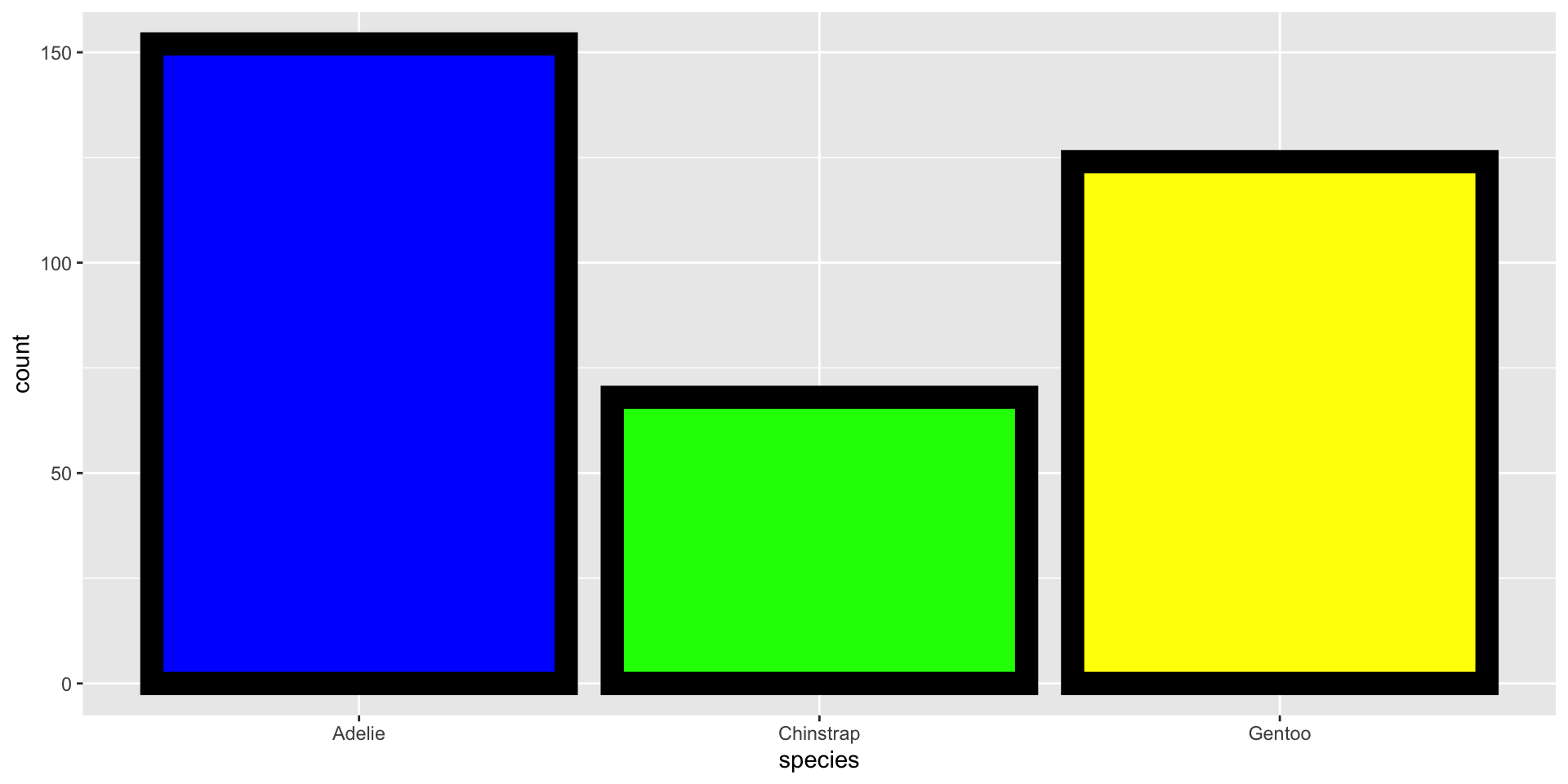
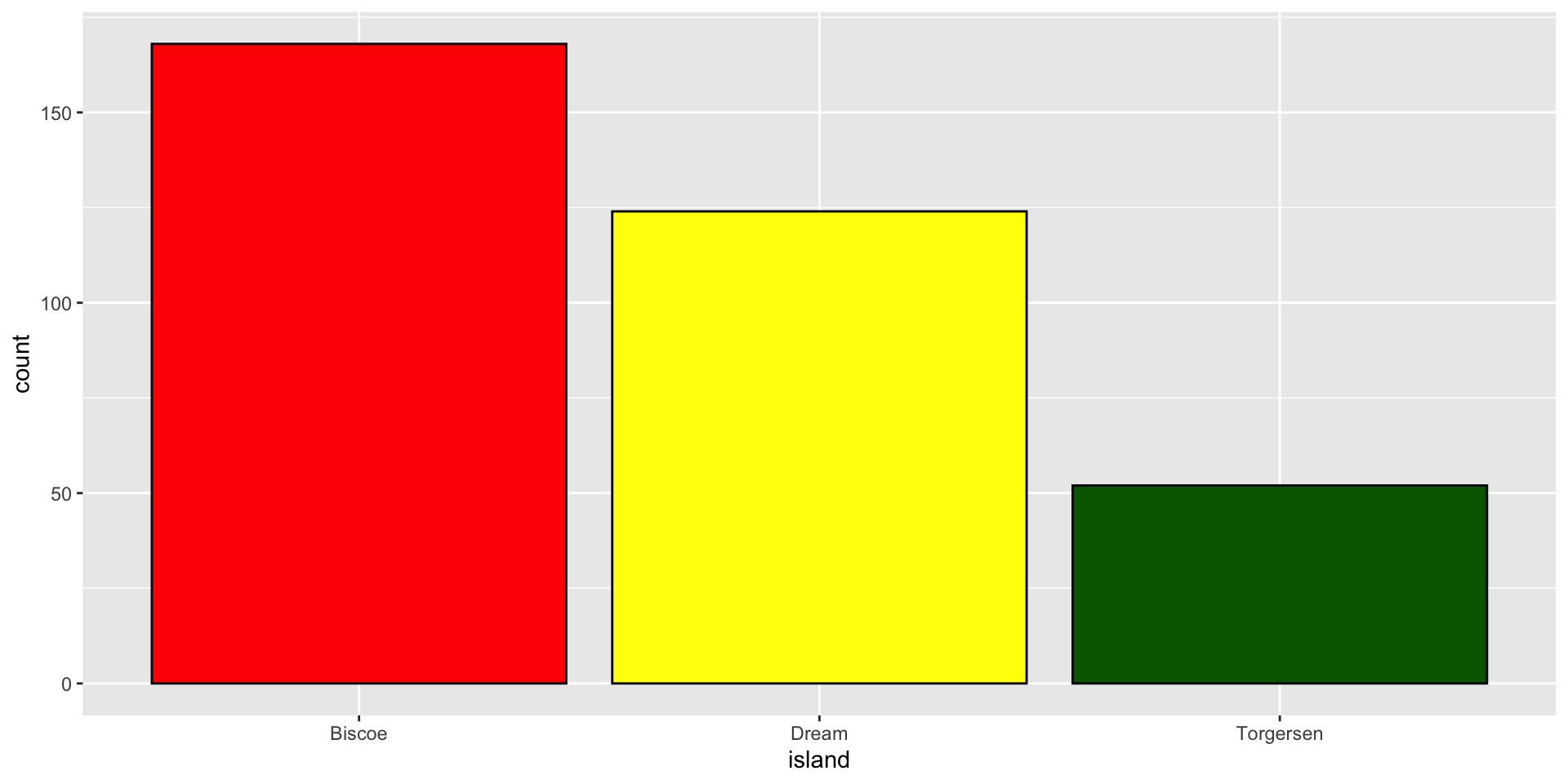
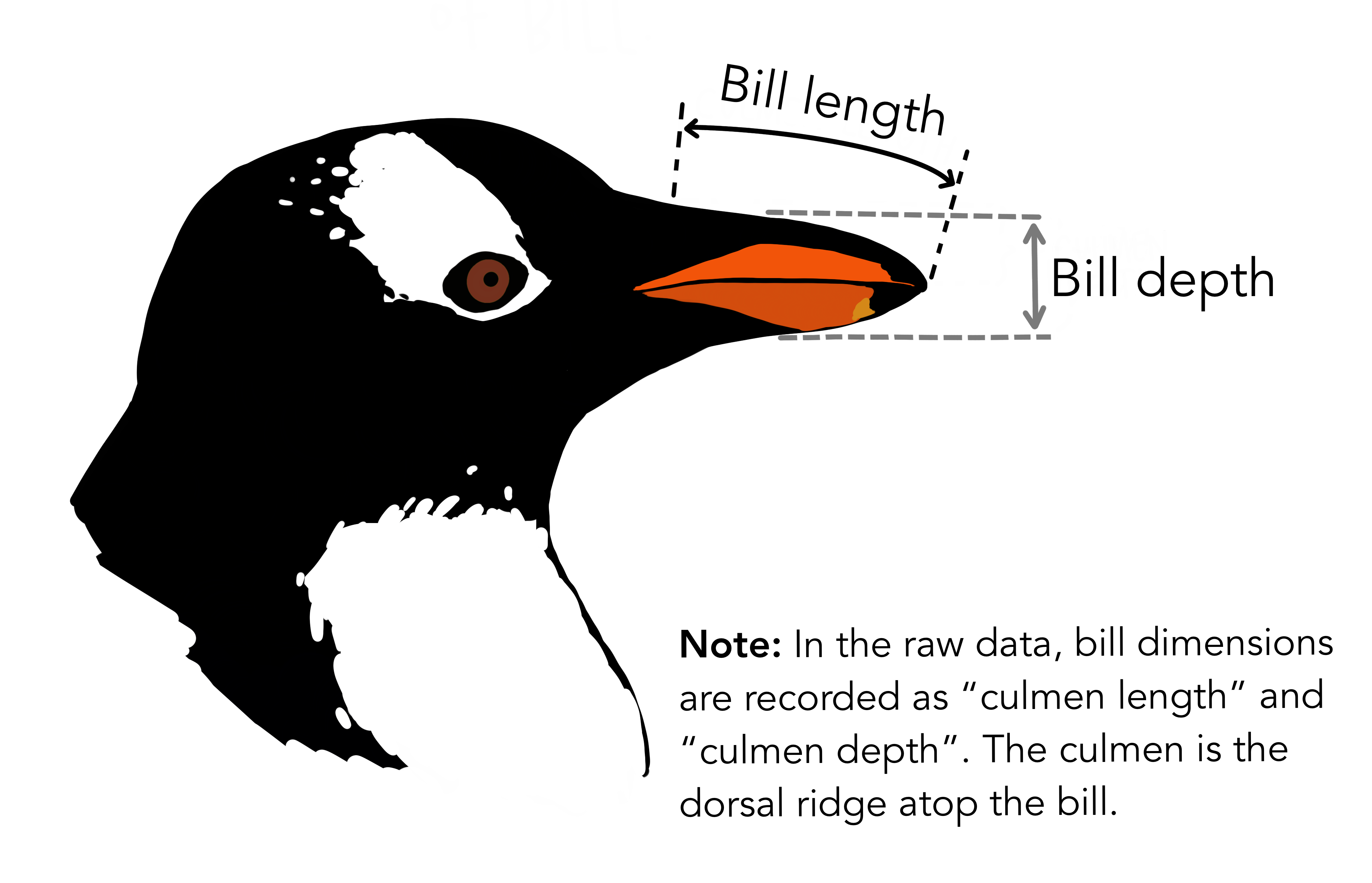
Data: penguins
Live on three island: Biscoe, Dream, & Torgersen.

Know Your Data
Import Data
Map Variables Aesthetics
Add Geometric Shapes
Key Components are:
Your data set,
A set of aesthetic mappings between variables in the data and visual properties, and
At least one layer which describes how to render each observation. Layers are usually created with a geom function.
🧠 YOUR TURN
05:00
Common Mistakes
Make sure that every
(is matched with a)and every"is paired with another".Console shows no results but a
+sign that means your code is incomplete and R is waiting for you to complete the code.in ggplot
+has to come at the end of the line, not the start
“Fill” Color
“Fill” Colors
“Fill” & “Color” Colors
🧠 YOUR TURN
05:00
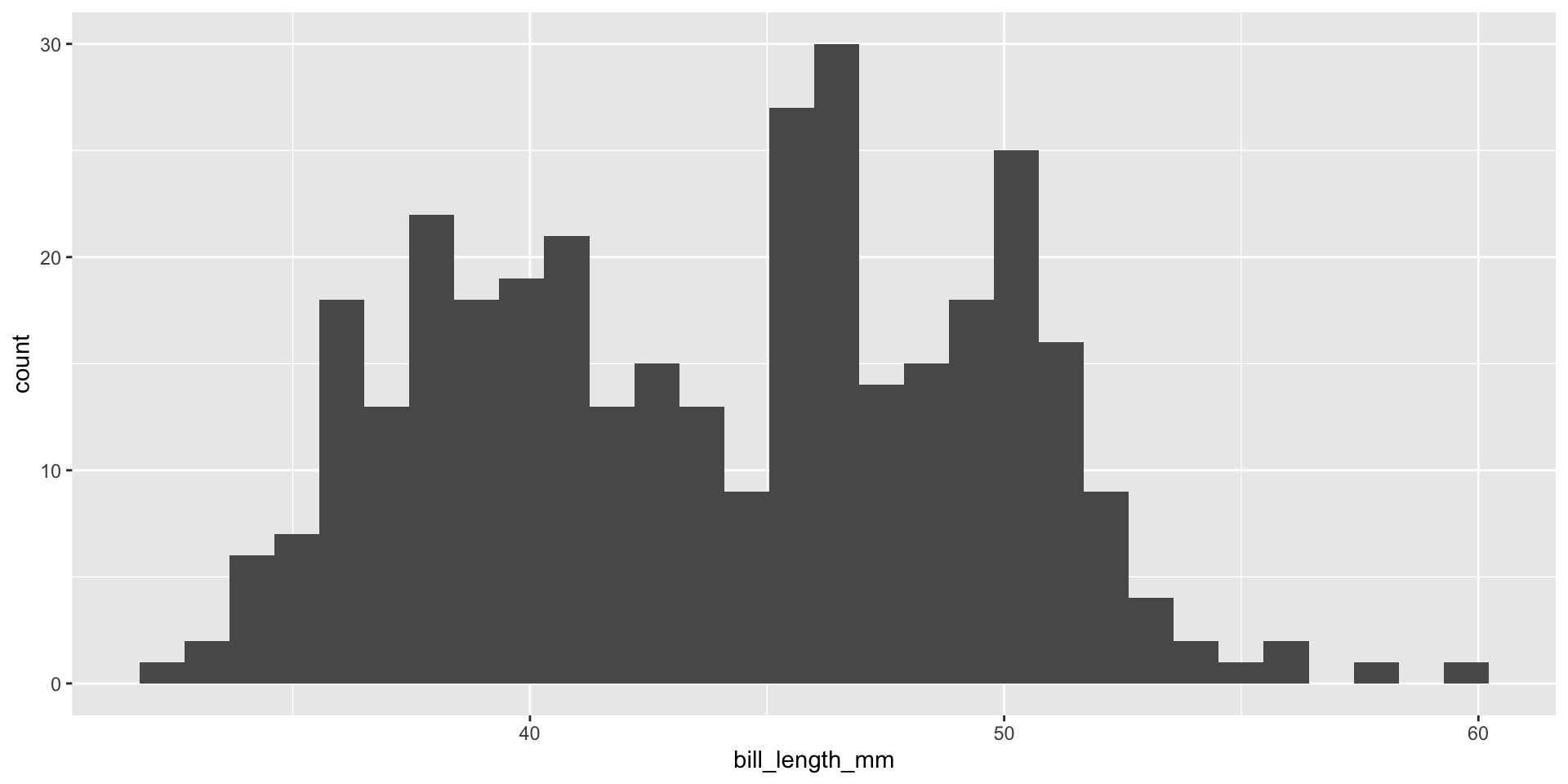
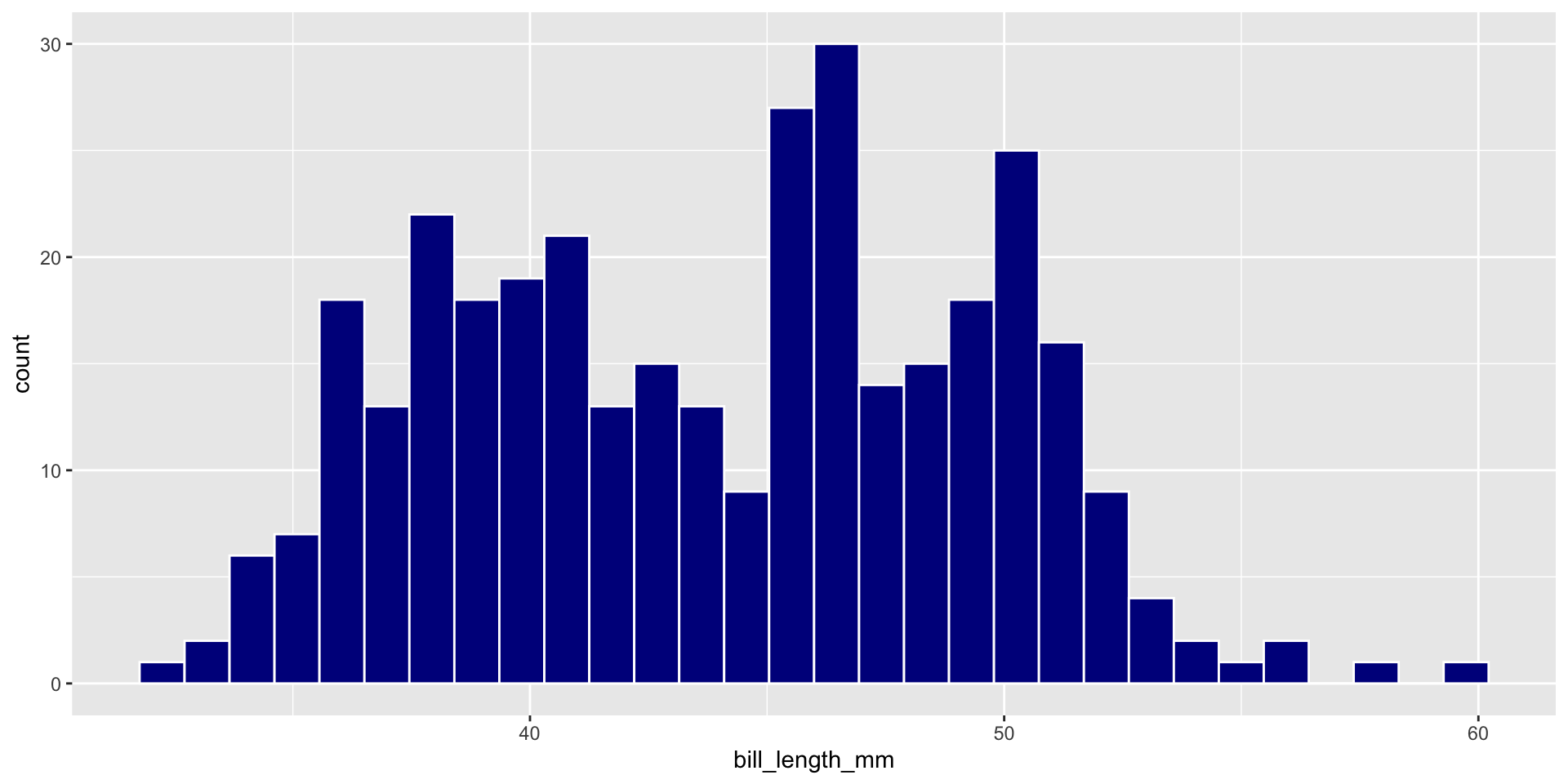
Plot A Continuous Variable
🧠 YOUR TURN
05:00
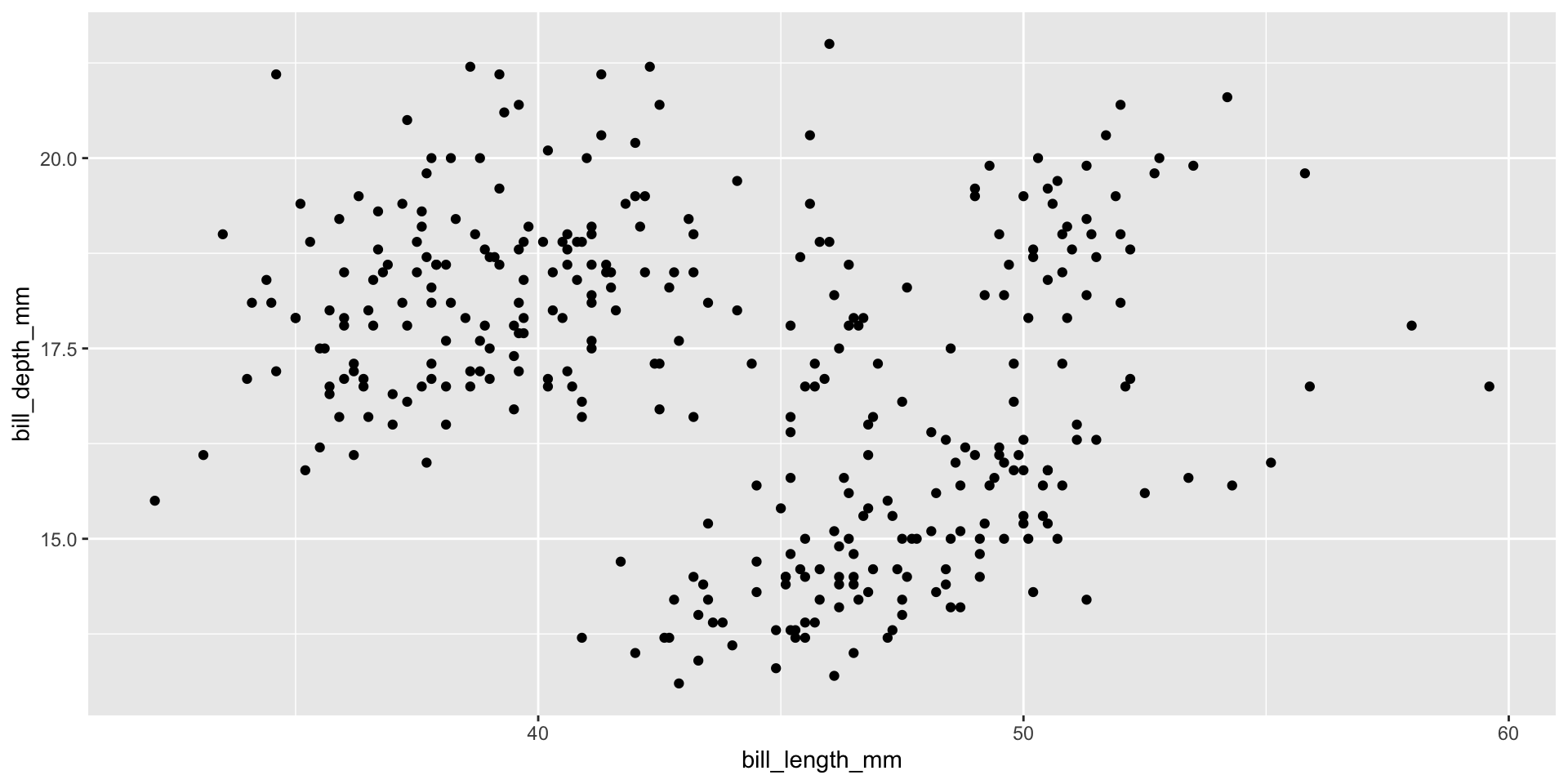
Two Continuous Variables
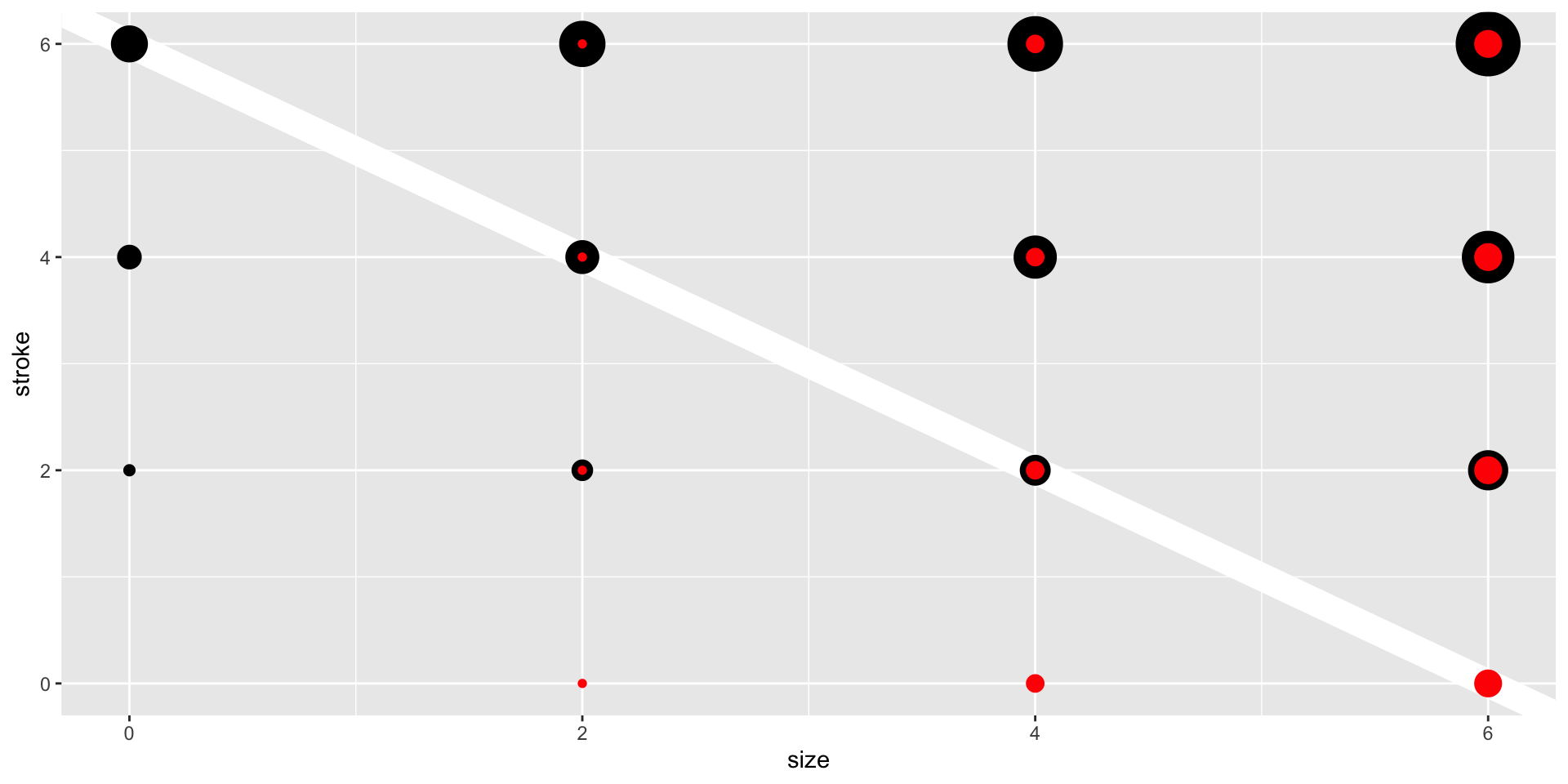
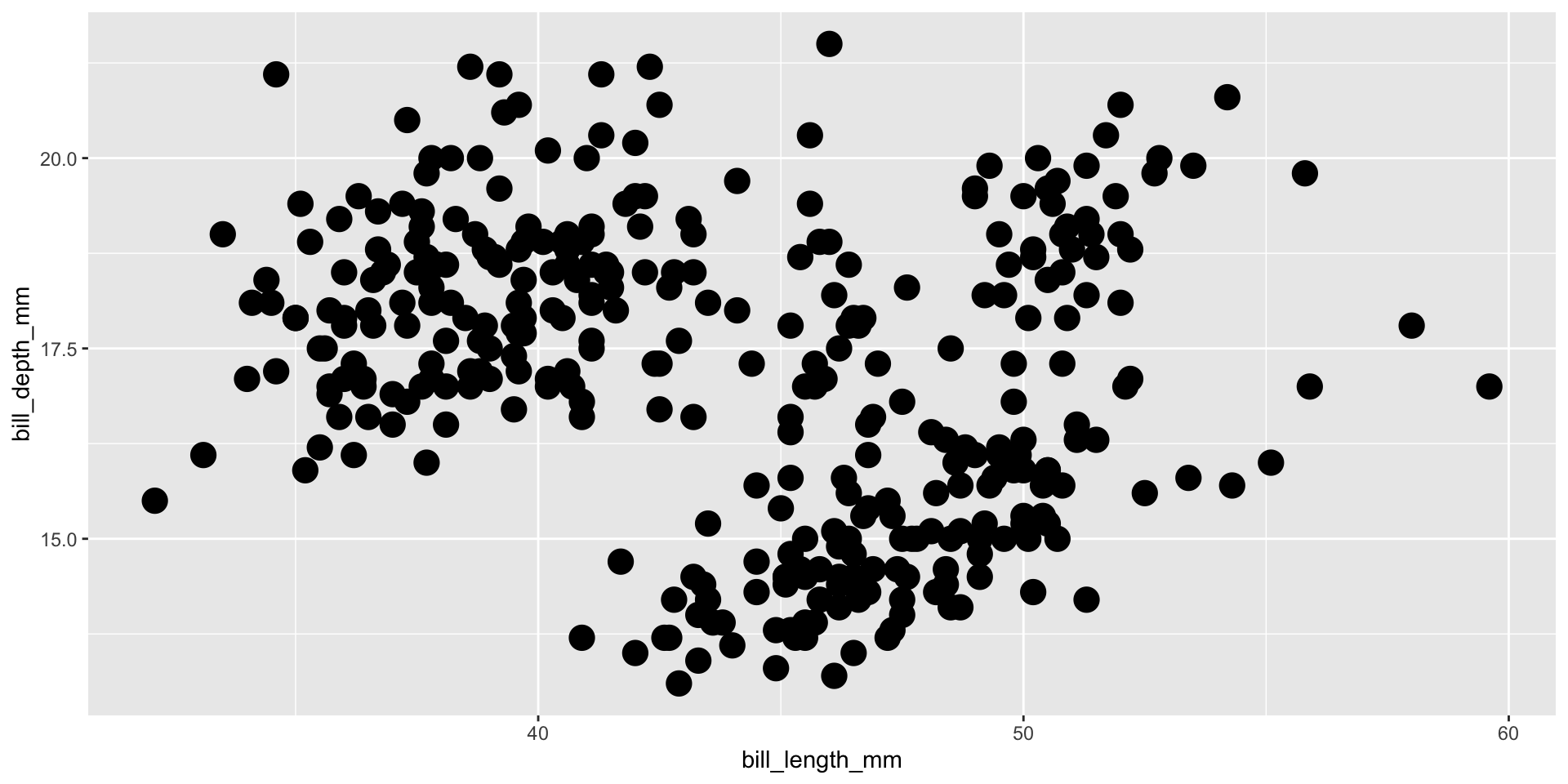
Geom Size
Geom Shape
🧠 YOUR TURN
05:00
Plot Two Factors/Categorical
Plot a Continuous and Factor
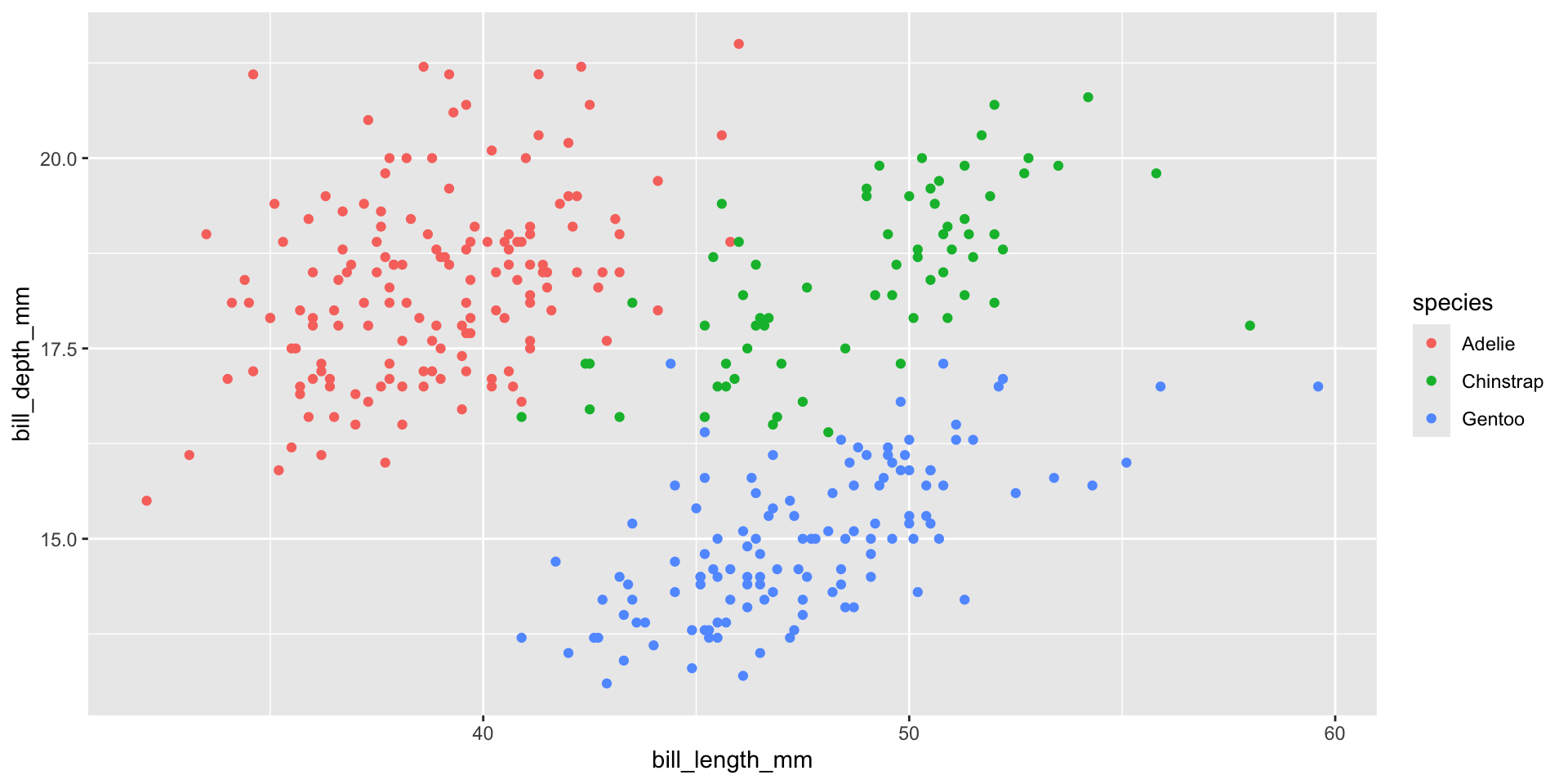
Two Continuous & a Factor
Two Continuous & a Factor
Write Labels
Title of the plot
Subtitle of the plot with more information
Title of the x-axis
Title of the y-axis
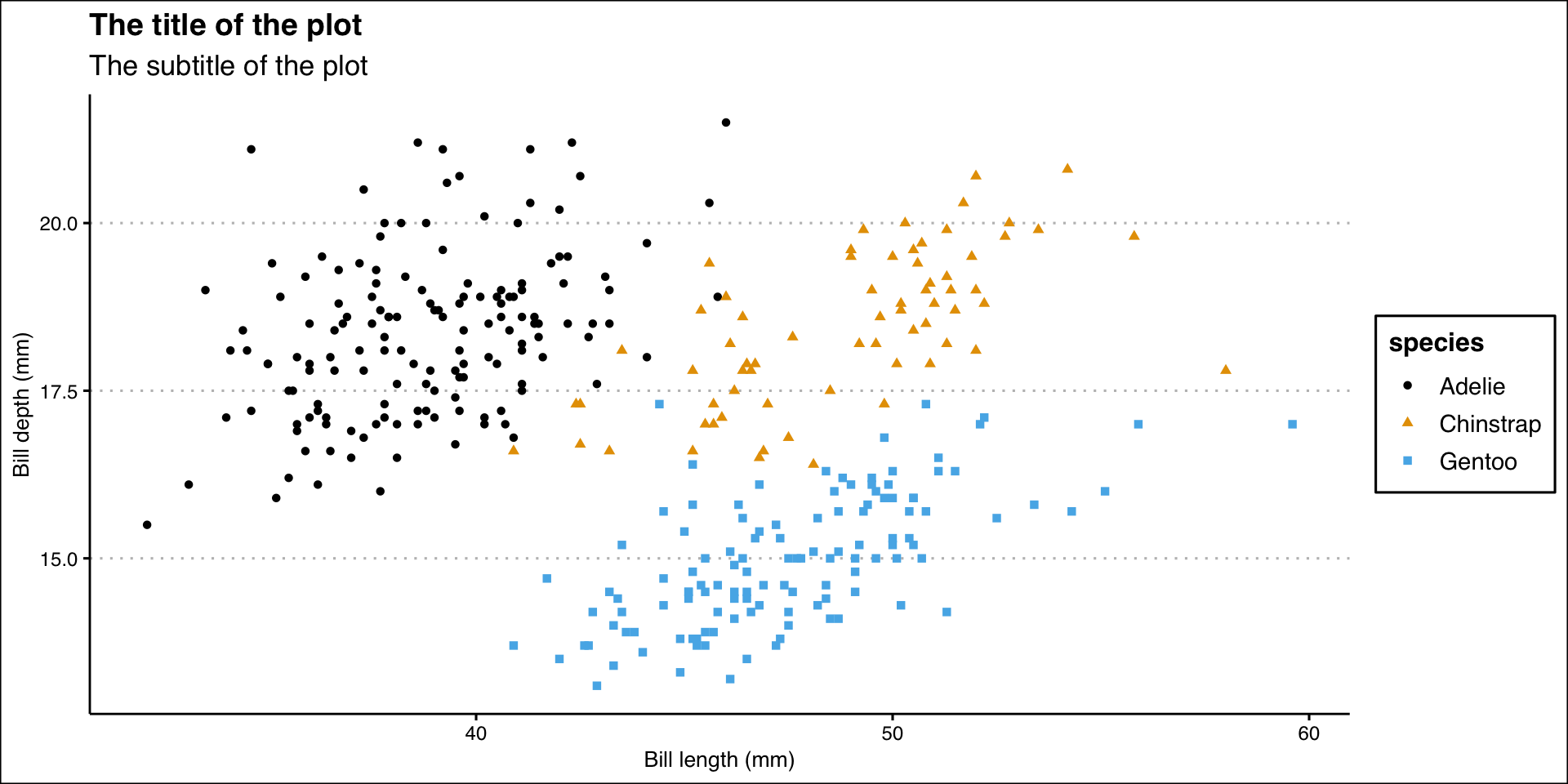
Different Shapes
Each level of the factor/category can be shown using a different shape of different color.
ggplot Extension Packages
GGThemes
Additional themes, scales, and geoms for ggplot2
Source: Learn more about ggthemes & ggthemes tutorial
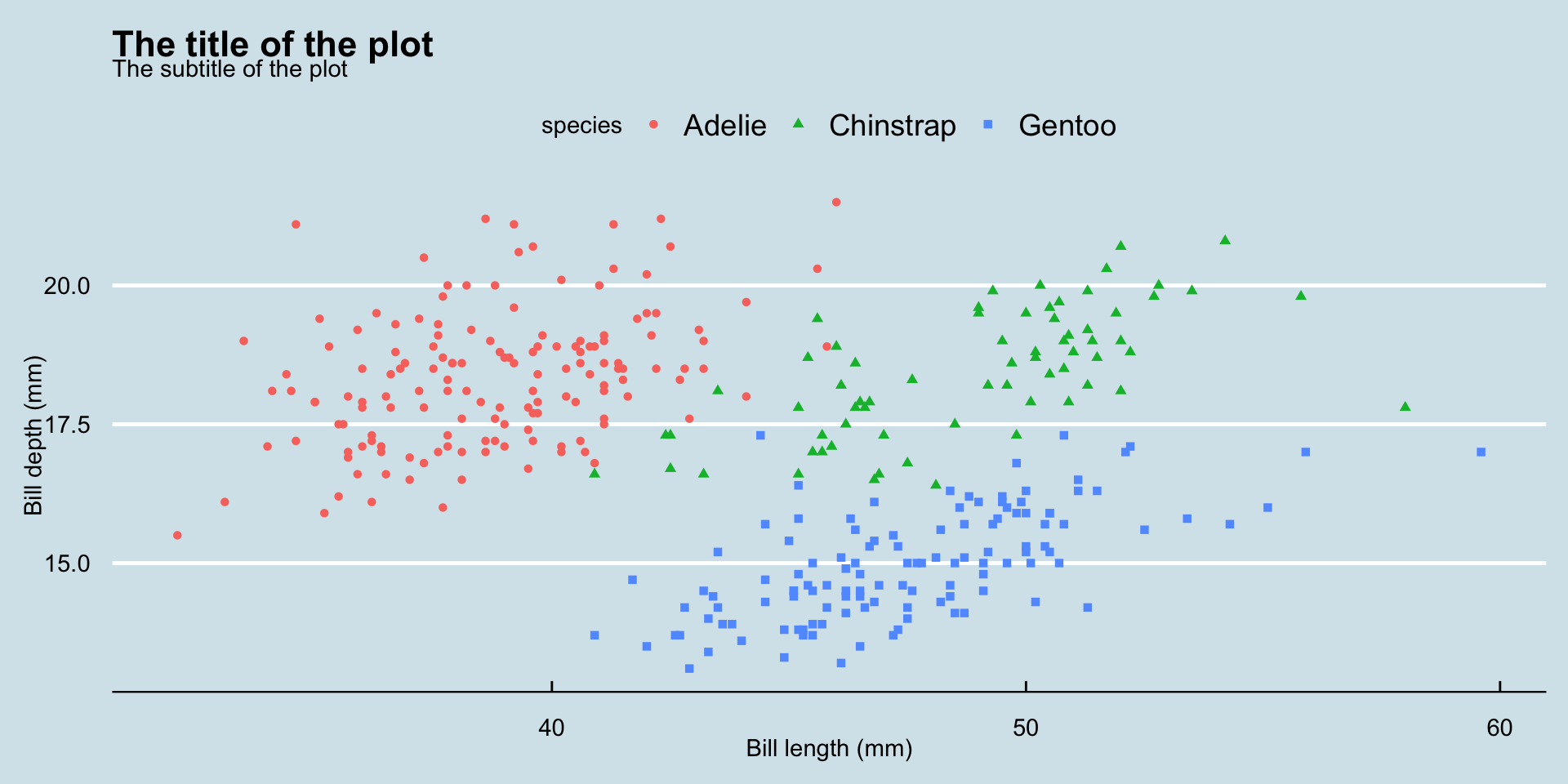
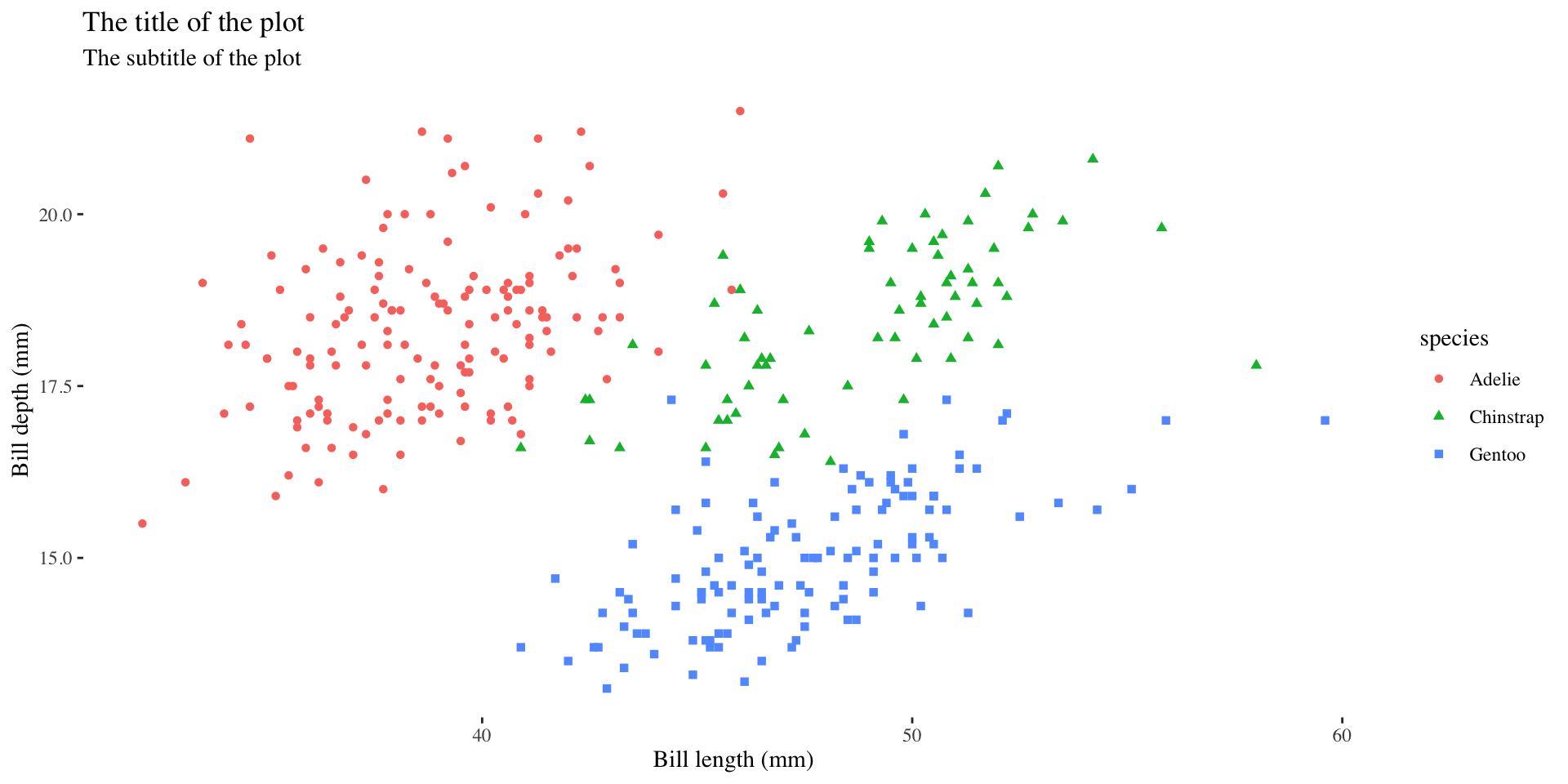
Theme Solarized
billplot <- ggplot(data = penguins,
mapping = aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(aes(color = species, shape = species)) +
labs(
title = "The title of the plot",
subtitle = "The subtitle of the plot",
x = "Bill length (mm)",
y = "Bill depth (mm)"
)
billplot + theme_solarized_2()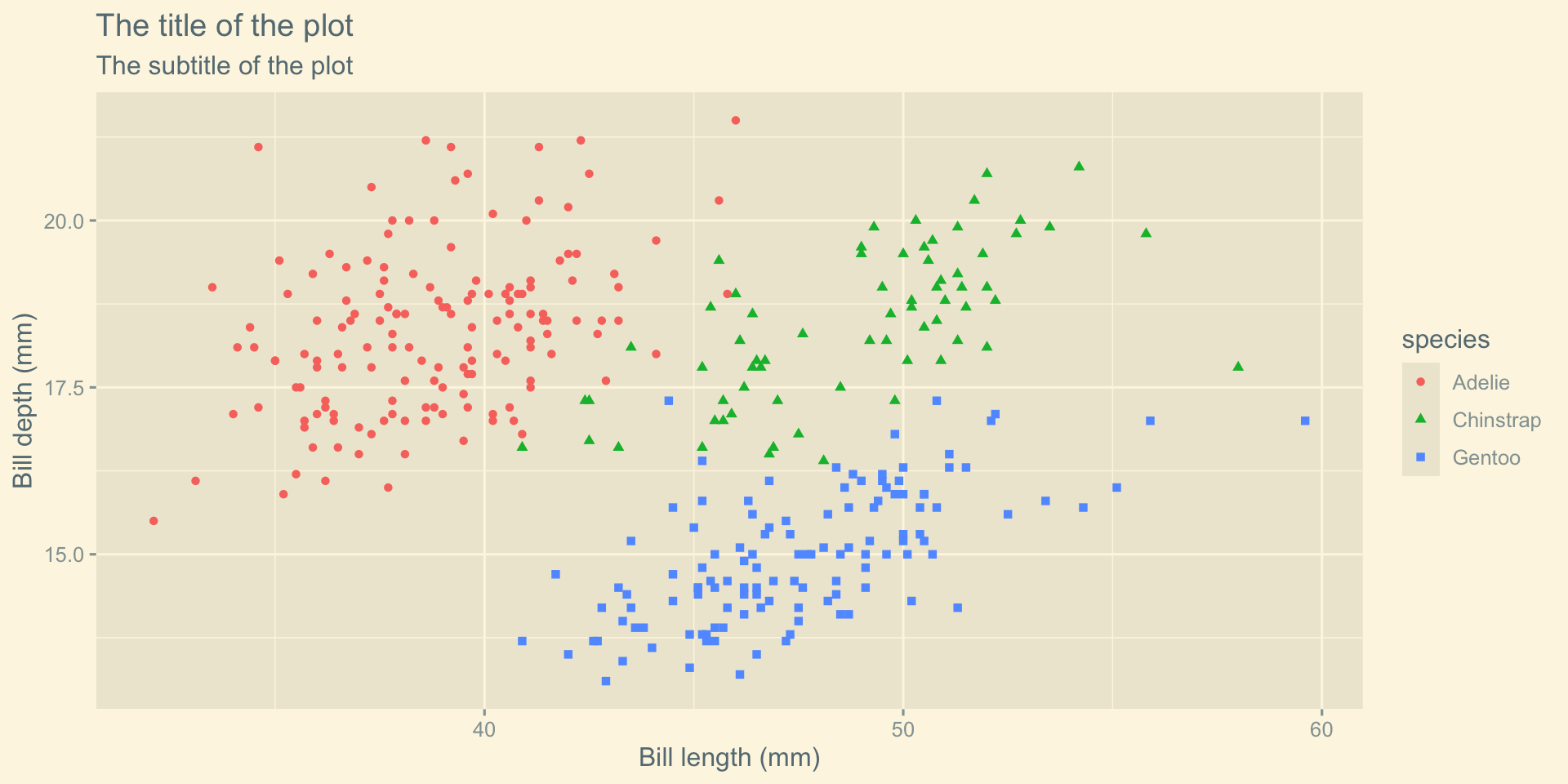
Theme Tufte
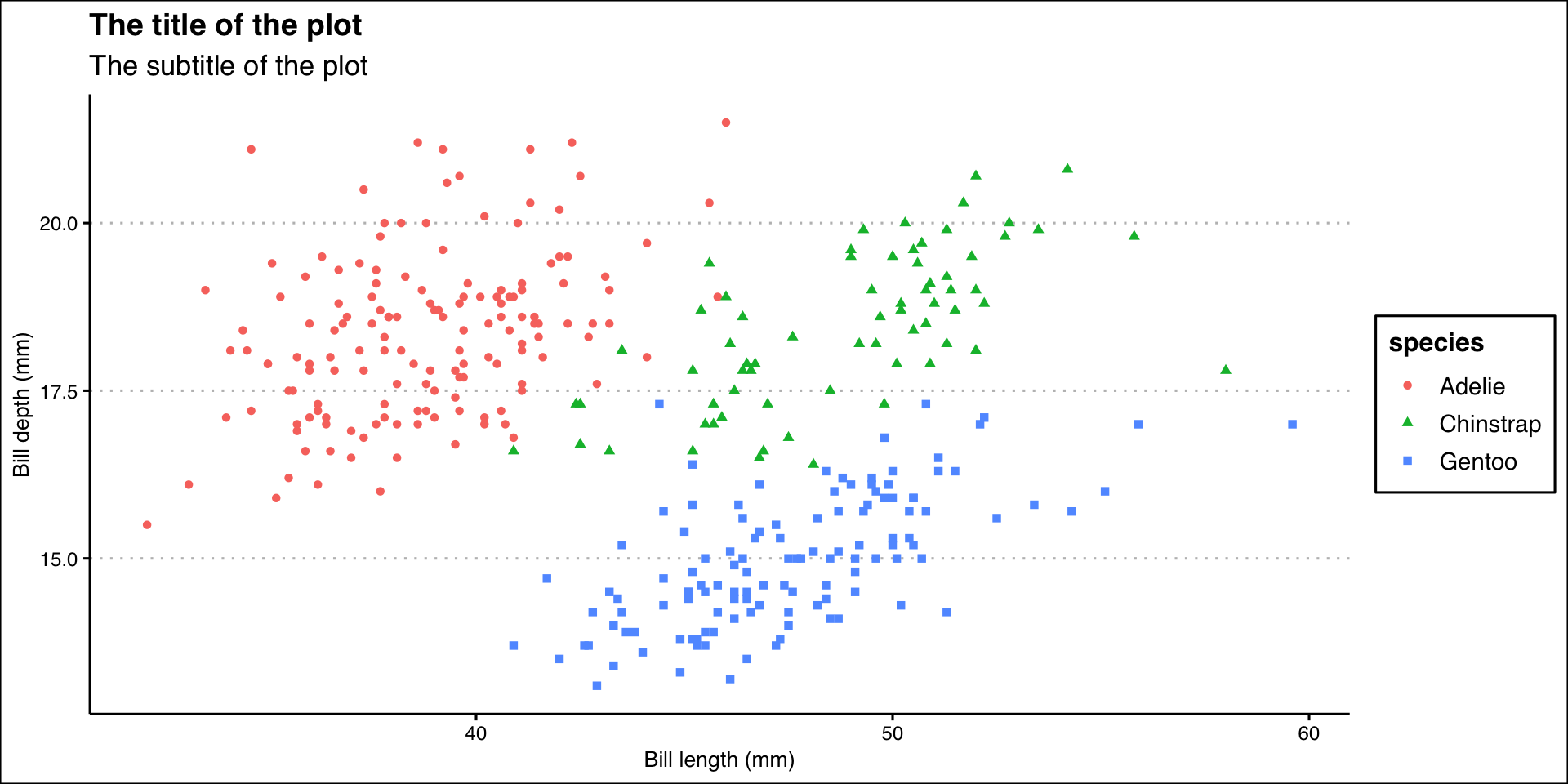
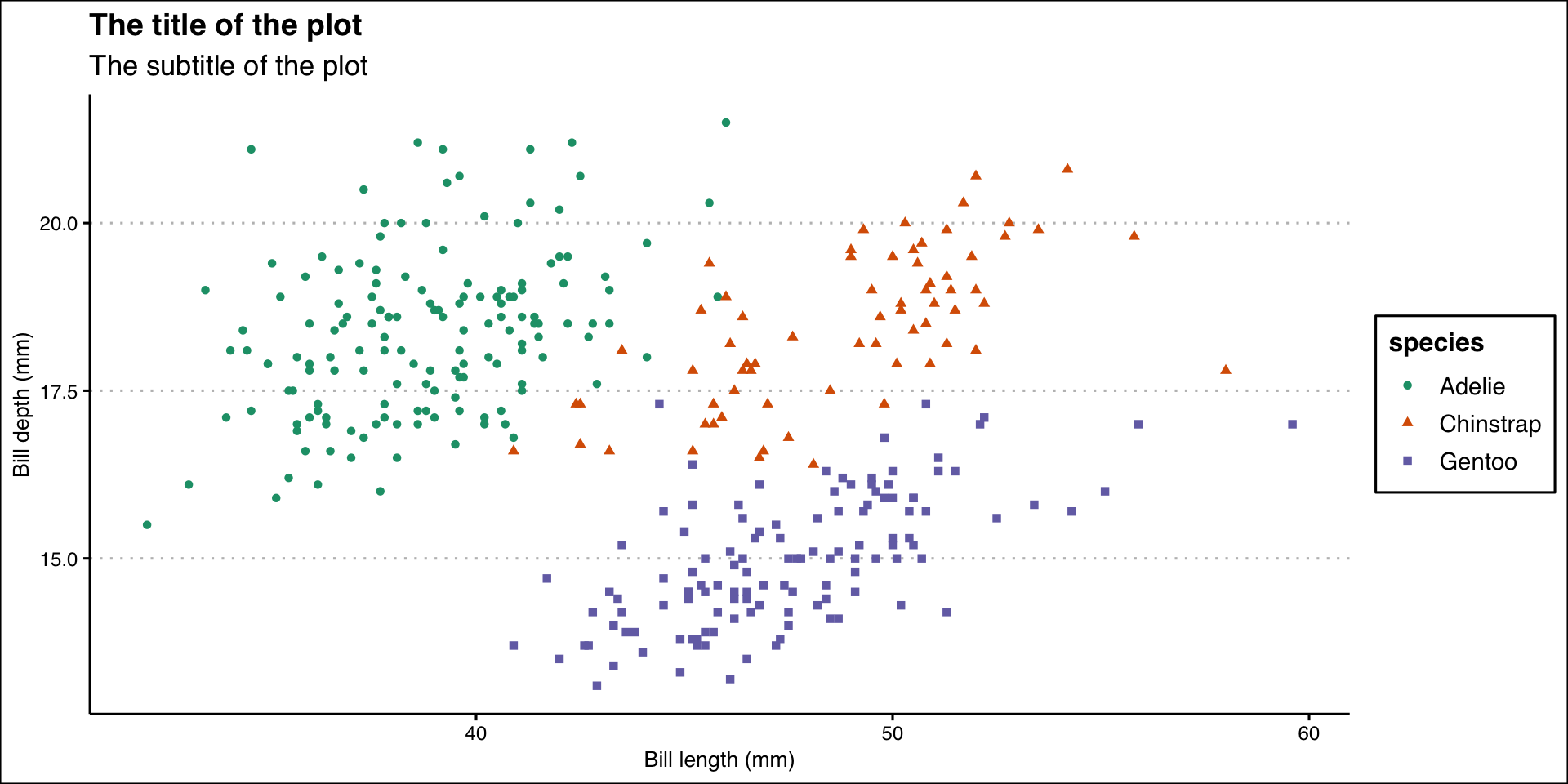
Theme Clean
🎨 Color Palette
Color Palette
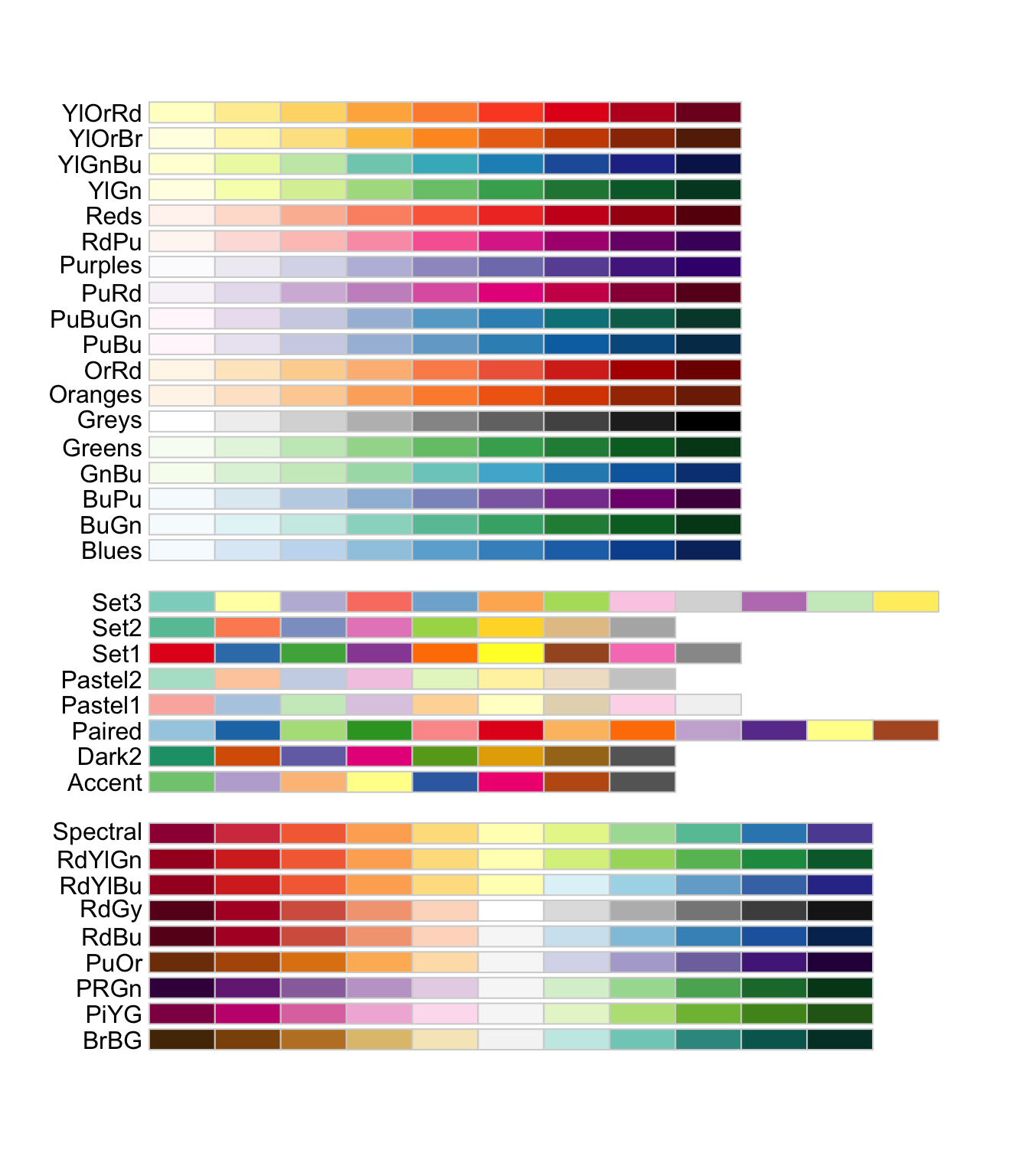
Color Palette RColorBrewer
Color Palette Wesanderson
[1] "BottleRocket1" "BottleRocket2" "Rushmore1"
[4] "Rushmore" "Royal1" "Royal2"
[7] "Zissou1" "Zissou1Continuous" "Darjeeling1"
[10] "Darjeeling2" "Chevalier1" "FantasticFox1"
[13] "Moonrise1" "Moonrise2" "Moonrise3"
[16] "Cavalcanti1" "GrandBudapest1" "GrandBudapest2"
[19] "IsleofDogs1" "IsleofDogs2" "FrenchDispatch"
[22] "AsteroidCity1" "AsteroidCity2" "AsteroidCity3" 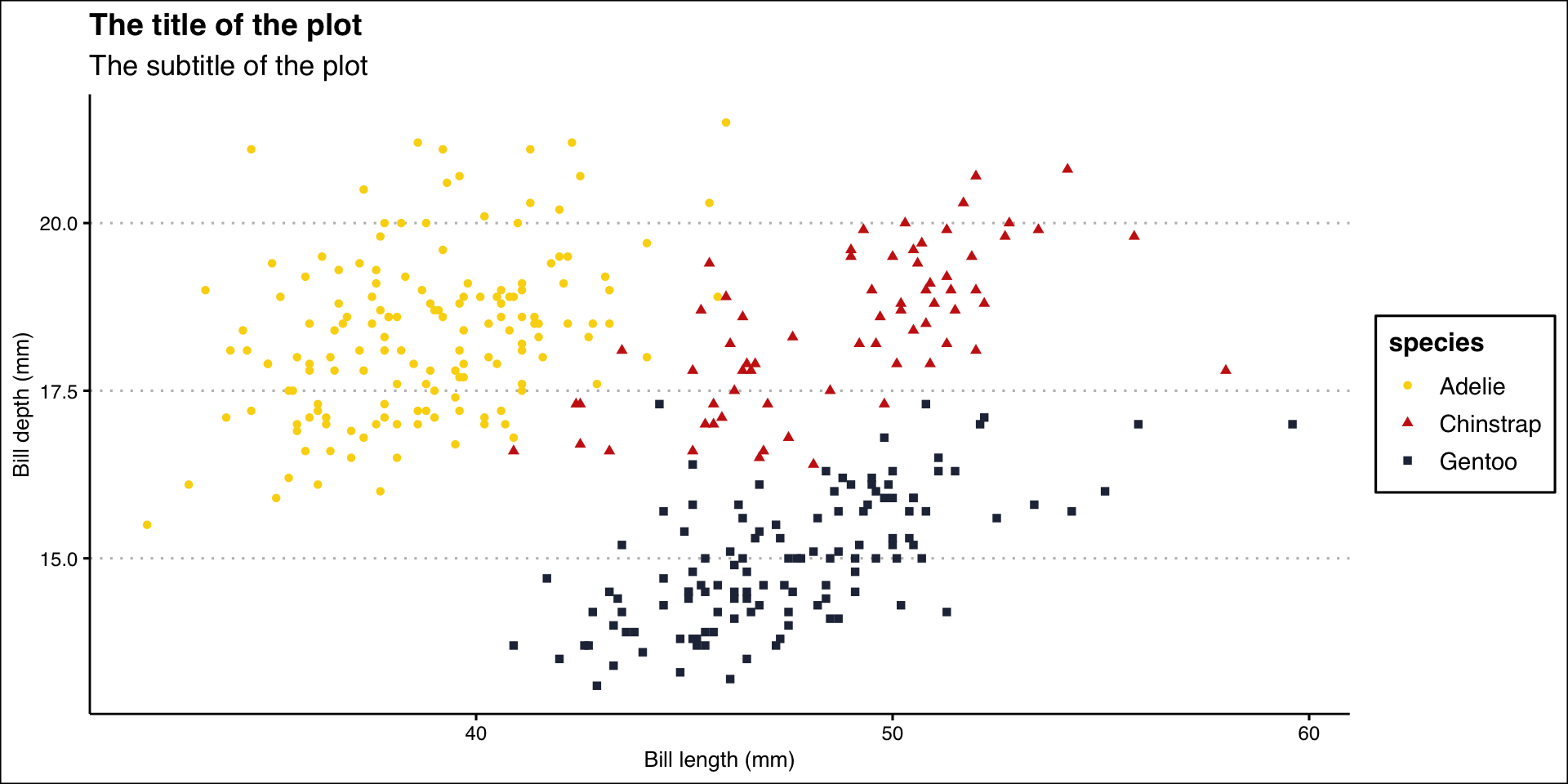
Export Plot
Export/save plot as pdf, jpg or png file.
ggplot(data = penguins,
mapping = aes(x = bill_length_mm, y = bill_depth_mm)) +
geom_point(aes(color = species, shape = species)) +
labs(
title = "The title of the plot",
subtitle = "The subtitle of the plot",
x = "Bill length (mm)",
y = "Bill depth (mm)"
) +
theme_clean() +
scale_color_manual(values = wes_palette("BottleRocket2", n = 3))
ggsave("penguins-plot.pdf")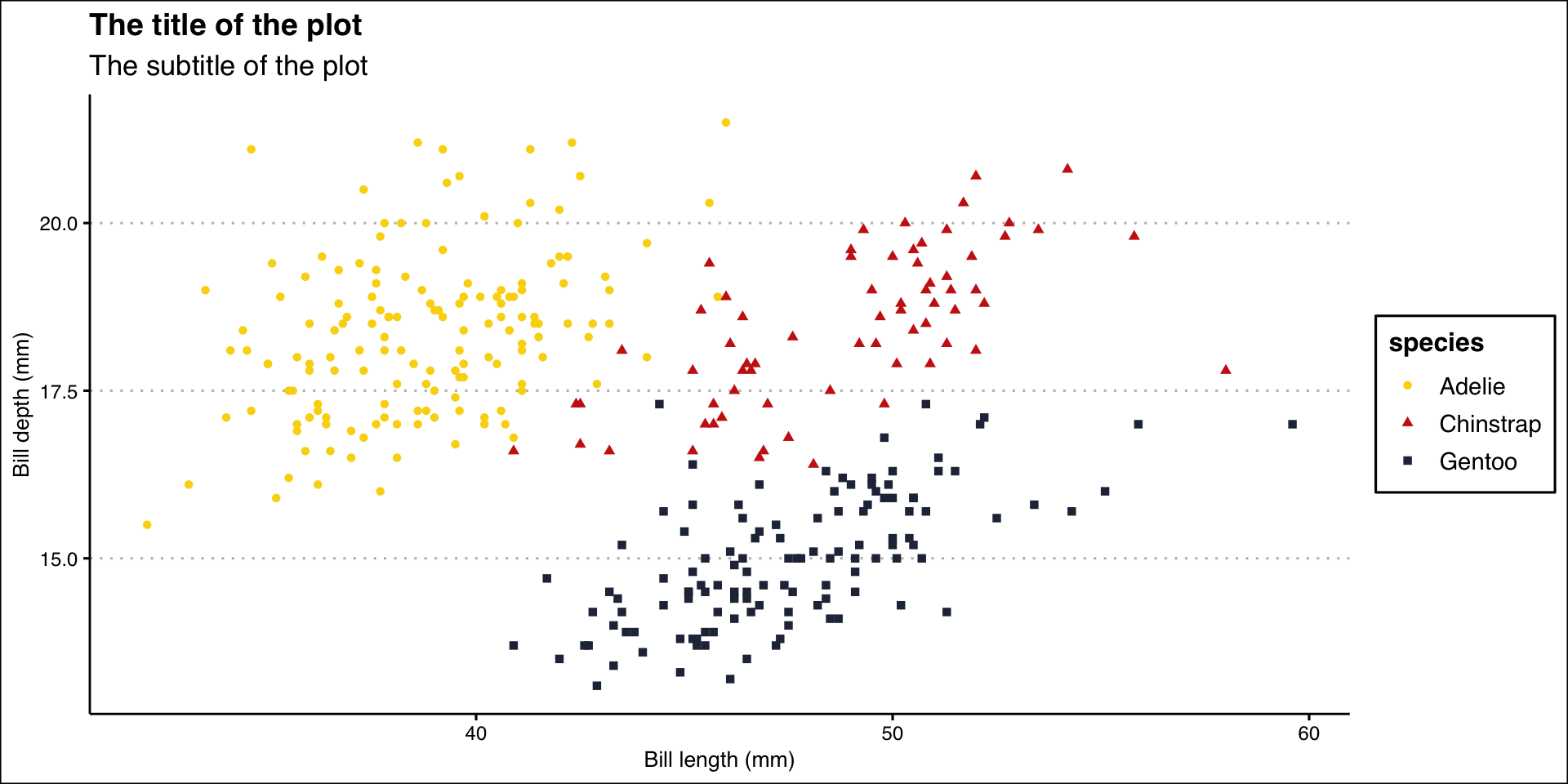
🧑🏽💻👨🏽💻
Question & Answer
🤯 Your Turn
1. What is ggplot2 used for in R?
- Data cleaning
- Data visualization
- Text mining
- Machine learning
🤯 Your Turn
2. In ggplot2, the function aes() is used for:
- Loading data
- Mapping variables to aesthetics like x, y, color
- Saving plots as images
- Applying statistical models
🤯 Your Turn
3. Which function is used to create a scatter plot in ggplot2?
- geom_bar()
- geom_line()
- geom_point()
- geom_boxplot()
🤯 Your Turn
4. In ggplot2, theme_minimal() is used to:
- Filter the dataset
- Apply a clean, minimal plot style
- Add a legend
- Change axis limits
🤯 Your Turn
5. Which package must be loaded to use ggplot2 functions?
- dplyr
- ggplot2
- tidyr
- plotly
🤩 Your Turn Answers
Correct answer: B) Data visualization
Correct answer: B) Mapping variables to aesthetics like x, y, color
Correct answer: C) geom_point()
Correct answer: B) Apply a clean, minimal plot style
Correct answer: B) ggplot2
thank You! IDSJ TEAM